To accompany the introduction of our llama antibody service we will be running this llama antibody blog. The first installment covers some of the differences seen in llama heavy chain antibodies.
Llama antibodies – small but fully functional
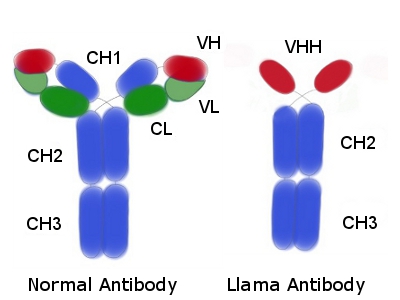
In the mid 1990s it was discovered that, in addition to conventional antibodies, llamas produce functional immunoglobulins that lack light chains and the first heavy chain constant region (CH1). The variable domain of these llama antibodies heavy chain homodimers (VHH) forms a smaller paratope then conventional antibodies (the latter use the variable light and heavy chains for this).
Despite the size of the llama antibody being approximately 15kDa, their specificities and affinities are comparable with those of conventional 150 kDa immunoglobulins. In some applications llama antibodies have advantages because of their size.
Llama antibodies – structural differences
As mentioned earlier, the llama VHH is a single domain that connects, via a hinge, to the Fc region. The VHH still has three complementary determining regions (CDR). However, it has been found that the in a llama antibody the CDR3 is much longer than the one in the mouse – in some cases up to 3 times longer. This longer llama CDR3 is sometimes stabilized by a disulphide bond between CDR3 and CDR2.
These difference mean that VHH can form rod-like structures, ideal for binding sites in cavities e.g. enzyme clefts. The CD3 of llama antibodies also manages to form convex structures that can cover the binding site. Conventional antibodies need relatively flat binding sites.
The next blog entries will look at application areas especially suited for llama antibodies.
Further reading:
- Hamers-Casterman C, Atarhouch T, Muyldermans S, Robinson G, Hamers C, Songa EB, Bendahman N, Hamers R. Naturally occurring antibodies devoid of light chains. Nature. 1993 Jun 3;363(6428):446-8. PubMed PMID: 8502296
- Muyldermans S, Atarhouch T, Saldanha J, Barbosa JA, Hamers R. Sequence and structure of VH domain from naturally occurring camel heavy chain immunoglobulins lacking light chains. Protein Eng. 1994 Sep;7(9):1129-35. PubMed PMID: 7831284.
- Harmsen MM, Ruuls RC, Nijman IJ, Niewold TA, Frenken LG, de Geus B. Llama heavy-chain V regions consist of at least four distinct subfamilies revealing novel sequence features. Mol Immunol. 2000 Aug;37(10):579-90. PubMed PMID: 11163394.
- Bond CJ, Marsters JC, Sidhu SS. Contributions of CDR3 to V H H domain stability and the design of monobody scaffolds for naive antibody libraries. J Mol Biol. 2003 Sep 19;332(3):643-55. PubMed PMID: 12963373.


